Motion of microobjects
in flows - application to fibers, polymers, DNA chains
Hydrodynamic
interactions between colloidal particles and polymeric chains are of great
interest in chemical, biomedical, and environmental engineering and science.
Examples include processes such as sedimentation, flotation, coagulation,
deposition, suspension rheology motion of
blood cells in an artery or vein, and
diffusion in. pores.
The aim of
the proposed subject is to introduce and to explore the existing algorithms for
computing hydrodynamic interactions between colloidal particles often bounded
by the outer walls, e.g. thin films, cylindrical microchannels.
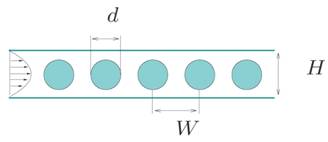
Particles
in cylindrical microchannel driven by parabolic flow
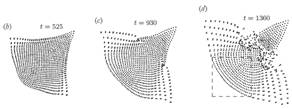
Evolution
of a force-driven square array of 1000 particles moving in the flat microchannel.
1)
A. Mongruel, N. Lecoq, E. Wajnryb, B. Cichocki, F. Feuillebois, Motion
of a sphero-cylindrical particle in a viscous fluid
in confined geometry, European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids (2011)
2) Marcin Kędzierski and Eligiusz Wajnryb, Precise multipole method for calculating many-body hydrodynamic
interactions in a microchannel, J. Chem. Phys. 133
(2010) 154105-1,11
3) B. Cichocki, E. Wajnryb, J. Bławzdziewicz, J. K. G. Dhont,
and P. R. Lang, The intensity correlation function in evanescent wave
scattering, .J. Chem. Phys. 132 (2010) 074704-1,12
4)
M.
Baron, J. Blawzdziewicz, and E. Wajnryb, Hydrodynamic Crystals: Collective Dynamics of
Regular Arrays of Spherical Particles in a Parallel-Wall Channel, PRL 100, 174502 (2008)
Contact:
dr hab. Eligiusz Wajnryb, ewajnryb@ippt.gov.pl